List comprehension
A list comprehension is a syntactic construct available in some programming languages for creating a list based on existing lists. It follows the form of the mathematical set-builder notation (set comprehension) as distinct from the use of map and filter functions.
Contents |
Overview
Consider the following example in set builder notation.
This can be read, "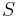 is the set of all numbers "2 times
is the set of all numbers "2 times  " where
" where  is an item in the set of natural numbers (
is an item in the set of natural numbers (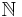 ), for which
), for which  squared is greater than
squared is greater than 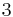 ."
."
In this annotated version of the example:
 is the variable representing members of an input set.
is the variable representing members of an input set.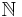 represents the input set, which in this example is the set of natural numbers
represents the input set, which in this example is the set of natural numbers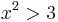 is a predicate function acting as a filter on members of the input set.
is a predicate function acting as a filter on members of the input set.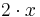 is an output function producing members of the new set from members of the input set that satisfy the predicate function.
is an output function producing members of the new set from members of the input set that satisfy the predicate function. brackets contain the expression
brackets contain the expression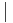
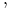 the vertical bar and the comma are separators.
the vertical bar and the comma are separators.
A list comprehension has the same syntactic components to represent generation of a list in order from an input list or iterator:
- A variable representing members of an input list.
- An input list (or iterator).
- An optional predicate expression.
- And an output expression producing members of the output list from members of the input iterable that satisfy the predicate.
The order of generation of members of the output list is based on the order of items in the input.
In Haskell's list comprehension syntax, this set-builder construct would be written similarly, as:
s = [ 2*x | x <- [0..], x^2 > 3 ]
Here, the list [0..] represents 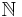 ,
, x^2>3 represents the predicate, and 2*x represents the output expression.
List comprehensions give results in a defined order (unlike the members of sets); and list comprehensions may generate the members of a list in order, rather than produce the entirety of the list thus allowing, for example, the previous Haskell definition of the members of an infinite list.
History
The SETL programming language (later 1960s) had a set formation construct, and the computer algebra system AXIOM (1973) has a similar construct that processes streams, but the first use of the term "comprehension" for such constructs was in Rod Burstall and John Darlington's description of their functional programming language NPL from 1977.
Smalltalk block context messages which constitute list comprehensions have been in that language since at least Smalltalk-80.
Burstall and Darlington's work with NPL influenced many functional programming languages during the 1980s but not all included list comprehensions. An exception was the influential pure lazy functional programming language Miranda which was released in 1985. The subsequently developed standard pure lazy functional language, Haskell, includes many of Miranda's features including list comprehensions. The Python programming language was heavily influenced by the pure lazy school of functional programming and adopted list comprehensions. Pure functional programming remains a niche while Python achieved wider adoption which introduced list comprehensions to a wider audience.
Comprehensions were proposed as a query notation for databases[1] and were implemented in the Kleisli database query language.[2]
Examples in different programming languages
The following provides a few examples of specific syntax used in programming languages.
Although the original example denotes an infinite list, few languages can express that, so in some of those cases we show how to take a subset of 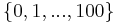 rather than a subset of
rather than a subset of 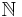 .
.
B-Prolog
L @= [Y : X in 1..100, [Y], (X*X>3, Y is 2*X)]
A list of the form [T : E1 in D1, ..., En in Dn, LocalVars, Goal] is interpreted as a list comprehension in calls to @=/2 and constraints. A list comprehension is translated into a foreach construct with an accumulator.
Clojure
Clojure generates infinite lazy sequences (similar to Haskell's lazy lists or Python's generators). Use take to get the first N results from the infinite sequence.
(take 20 (for [x (iterate inc 0) :when (> (* x x) 3)] (* 2 x)))
Common Lisp
List comprehensions can be expressed with the loop macro's collect keyword. Conditionals are expressed with if, as follows:
(loop for x from 0 to 100 if (> (* x x) 3) collect (* 2 x))
An infinite lazy sequence can be created in a variety of ways, such as the CLOS object system or a yield macro.
Erlang
The same example in Erlang:
S = [2*X || X <- lists:seq(0,100), X*X > 3].
F#
The F# generator comprehension has the list comprehension syntax elements. Generator comprehensions can be used to generate Lists, Sequences (lazy lists) and Arrays (not discussed here).
Generators are of the form [for x in collection do ... yield expr] for lists and seq {for x in collection do ... yield expr} for sequences. For example:
GeSHi Error: GeSHi could not find the language fsharp (using path /usr/share/php-geshi/geshi/) (code 2)
You need to specify a language like this: <source lang="html4strict">...</source>
Supported languages for syntax highlighting:
abap, actionscript, actionscript3, ada, apache, applescript, apt_sources, asm, asp, autoit, avisynth, bash, basic4gl, bf, bibtex, blitzbasic, bnf, boo, c, c_mac, caddcl, cadlisp, cfdg, cfm, cil, cmake, cobol, cpp, cpp-qt, csharp, css, d, dcs, delphi, diff, div, dos, dot, eiffel, email, erlang, fo, fortran, freebasic, genero, gettext, glsl, gml, gnuplot, groovy, haskell, hq9plus, html4strict, idl, ini, inno, intercal, io, java, java5, javascript, kixtart, klonec, klonecpp, latex, lisp, locobasic, lolcode, lotusformulas, lotusscript, lscript, lsl2, lua, m68k, make, matlab, mirc, modula3, mpasm, mxml, mysql, nsis, oberon2, objc, ocaml, ocaml-brief, oobas, oracle11, oracle8, pascal, per, perl, php, php-brief, pic16, pixelbender, plsql, povray, powershell, progress, prolog, properties, providex, python, qbasic, rails, rebol, reg, robots, ruby, sas, scala, scheme, scilab, sdlbasic, smalltalk, smarty, sql, tcl, teraterm, text, thinbasic, tsql, typoscript, vb, vbnet, verilog, vhdl, vim, visualfoxpro, visualprolog, whitespace, whois, winbatch, xml, xorg_conf, xpp, z80
Falcon
The "comp" generic method family provides wide support for comprehension. For example, the "mfcomp" method can be applied to an array:
s = [].mfcomp( { i => if i*i > 3: return 2*i; return oob(1)}, [1:101] )
Falcon can also use functional generators to provide input lists. For example, the following code uses a continuation to create a set of pairs.
gen = Continuation( function( max, c )
i = 0
while i < max: c(++i)
return oob(0)
end )
data = [10,11,12]
s = Set().mfcomp( {x, y => x+y}, .[gen 3], data )
Method "comp" was introduced in version 0.9.6, and methods "mcomp" and "mfcomp" in version 0.9.6.2.
Haskell
Please refer to the main example in the overview.
s = [ 2*x | x <- [0..], x^2 > 3 ]
Here, the list [0..] generates natural numbers one by one which get bound to variable x, x^2>3 represents the predicate that either accepts or rejects a given variable's value, and 2*x represents the result expression. There might be several generators and test predicates in one list compehension expression in Haskell, in effect defining nested loops, e.g.:
s = [ 2*x*y | x <- [0..], x^2 > 3, y <- [1,3..x], y^2 < 100-x^2] -- for each x from 0 by 1: -- if x^2 > 3: -- for each y from 1 by 2 upto x: -- if y^2 < 100 - x^2: -- produce 2*x*y
The above expression becomes unproductive ("stuck") at some point, when new xs keep being generated only to be rejected later on. This is so because any test can only reject a value it is given, not any future ones (there is no cut mechanism here, in Prolog terms - a generator in general might produce its values unordered, like e.g. the above expression itself). This can be delt with using bounded list generators always or by enclosing a generator inside a take or takeWhile call, limiting the amount of generated values.
JavaFX
Using the for statement and a boolean expression:
var s = for (i in [1..100][n | n*n > 3]) { 2*i }
JavaScript 1.8
Number.prototype.__iterator__=function(){for (var i=0; i<this; i++) yield i} var s = [2*i for (i in 101) if (i*i>3)]
Or, without prototyping the Number object,
var range = function(start,end){for (var i=start; i<=end; i++) yield i} var s = [2*i for (i in range(0,100)) if (i*i>3)]
Mathematica
Mathematica supports multiple programming styles and allows the programmer to implement using a mix of styles or only one style. Using the 'functional style' and a 'pure function' (aka 'code block' or 'lambda') :
S = Select[Range[0, 100], (# ^ 2 > 3 &) ]
and
S = Cases[ Range[0, 100], e_ /; e ^2 > 3]
A more 'procedural style' :
f[x_] := x^2 > 3; Select[ Range[0, 100], f ]
Using the 'rules style' of programming, the equivalent example becomes:
S = n /. e_ /; e ^2 < 3 -> 0; S = Select[S, (# > 0 &)]
Naturally, this can be done using the powerful symbolic notation as well, which uses actual mathematical symbols in a computable manner.
OCaml
OCaml Batteries Included has uniform comprehension syntax for lists, arrays, enumerations (like streams), lazy lists (like lists but evaluated on-demand), sets, hashtables, etc.
Comprehension are of the form [? expression | x <- enumeration ; condition; condition ; ... ?].
For instance,
# [? 2 * x | x <- 0 -- max_int ; x * x > 3 ?];; - : int Enum.t = <abstr>
or, to compute a list,
# [? List: 2 * x | x <- 0 -- 5 ; x * x > 3 ?];; - : int list = [4; 6; 8; 10]
or, to compute a set,
# [? PSet: 2 * x | x <- 0 -- 5 ; x * x > 3 ?];; - : int PSet.t = <abstr>
etc.
Octave
GNU Octave can do list (vector) comprehensions in the form (vector expression)(vector condition).
For example,
octave:1> x=0:100; s=(2*x)(x.**2<3)
s =
0 2
Pure
The same example in Pure:
s = [2*n | n=1..100; n*n > 3];
Python
The Python programming language has a corresponding syntax for expressing list comprehensions. The near-equivalent in Python to the example above is as follows:
S = [2 * x for x in range(101) if x ** 2 > 3]
List comprehensions were introduced in Python version 2.0.[3]
A generator expression may be used in Python versions 2.4 and above to achieve functional equivalence with S using a generator to iterate a (finite or infinite) sequence:
from itertools import count S = (2 * x for x in count() if x ** 2 > 3)
Racket
Racket provides functional versions of for-loops, which are essentially list comprehension syntax:
The imperative for can also be used, combined with Racket's generator library to produce an infinite generator:
Scala
Using the for-comprehension:
val s = for (x <- Stream.from(0); if x*x > 3) yield 2*x
Scheme
Although there is no standard list comprehension syntax in R5RS, many implementations provide an extension for this. For example, in Chicken Scheme:
There is also a portable library SRFI/42 "Eager Comprehensions", which in particular includes list comprehensions:
; example import into Racket Scheme
Smalltalk
((1 to: 100) select: [:x|x*x>3]) collect: [:x|2*x]
Visual Prolog
S = [ 2*X || X = std::fromTo(1, 100), X^2 > 3 ]
PowerShell
0..100 | Where {$_ * $_ -gt 3} | ForEach {$_ * 2}
Similar constructs
Monad comprehension
In Haskell, a monad comprehension is a generalization of the list comprehension to other monads in functional programming.
Set comprehension
Version 3.x and 2.7 of the Python language introduces syntax for set comprehensions. Similar in form to list comprehensions, set comprehensions generate Python sets instead of lists.
>>> s = {v for v in 'ABCDABCD' if v not in 'CB'} >>> print(s) {'A', 'D'} >>> type(s) <class 'set'> >>>
Racket set comprehensions generate Racket sets instead of lists.
"ABCDABCD""CB"
Dictionary comprehension
Version 3.x and 2.7 of the Python language introduced a new syntax for dictionary comprehensions, similar in form to list comprehensions but which generate Python dicts instead of lists.
>>> s = {key: val for key, val in enumerate('ABCD') if val not in 'CB'} >>> s {0: 'A', 3: 'D'} >>>
Racket hash table comprehensions generate Racket hash tables (one implementation of the Racket dictionary type).
"ABCD""CB"
Parallel list comprehension
The Glasgow Haskell Compiler has an extension called parallel list comprehension (also known as zip-comprehension) that permits multiple independent branches of qualifiers within the list comprehension syntax. Whereas qualifiers separated by commas are dependent ("nested"), qualifier branches separated by pipes are evaluated in parallel (this does not refer to any form of multithreadedness: it merely means that the branches are zipped).
-- regular list comprehension a = [(x,y) | x <- [1..5], y <-[3..5]] -- [(1,3),(1,4),(1,5),(2,3),(2,4) ... -- zipped list comprehension b = [(x,y) | (x,y) <- zip [1..5] [3..5]] -- [(1,3),(2,4),(3,5)] -- parallel list comprehension c = [(x,y) | x <- [1..5] | y <- [3..5]] -- [(1,3),(2,4),(3,5)]
Racket's comprehensions standard library contains parallel and nested versions of its comprehensions, distinguished by "for" vs "for*" in the name. For example, the vector comprehensions "for/vector" and "for*/vector" create vectors by parallel versus nested iteration over sequences. The following is Racket code for the Haskell list comprehension examples.
In Python we could do as follows:
# regular list comprehension >>> a = [(x, y) for x in range(1, 6) for y in range(3, 6)] [(1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 3), (2, 4), ... # parallel/zipped list comprehension >>> b = [x for x in zip(range(1, 6), range(3, 6))] [(1, 3), (2, 4), (3, 5)]
XQuery and XPath
Like the original NPL use, these are fundamentally database access languages.
This makes the comprehension concept more important, because it is computationally infeasible to retrieve the entire list and operate on it (the initial 'entire list' may be an entire XML database).
In XPath, the expression:
/library/book//paragraph[@style='first-in-chapter']
is conceptually evaluated as a series of "steps" where each step produces a list and the next step applies a filter function to each element in the previous step's output.[4]
In XQuery, full XPath is available, but FLWOR statements are also used, which is a more powerful comprehension construct.[5]
for $b in //book
where $b[@pages < 400]
order by $b//title
return
<shortBook>
<title>{$b//title}</title>
<firstPara>{($book//paragraph)[1]}</firstPara>
</shortBook>
Here the XPath //book is evaluated to create a sequence (aka list); the where clause is a functional "filter", the order by sorts the result, and the <shortBook>...</shortBook> XML snippet is actually an anonymous function that builds/transforms XML for each element in the sequence using the 'map' approach found in other functional languages.
So, in another functional language the above FLWOR statement may be implemented like this:
map(
newXML(shortBook, newXML(title, $1.title), newXML(firstPara, $1...))
filter(
lt($1.pages, 400),
xpath(//book)
)
)
LINQ in C#
C# 3.0 has a group of related features called LINQ, which defines a set of query operators for manipulating list-like structures (object enumerations, SQL datasets, …). On top of these operators it offers a comprehension syntax, reminiscent of SQL:
var s = from x in Enumerable.Range(0, 100) where x*x > 3 select x*2;
C++
List comprehensions can be constructed using the C++ STL algorithms remove_copy_if to select elements in a list and for_each to transform them.
#include <algorithm> #include <list> int linspace() { static int i=1; return i++; } bool sqrle3(int x) { return x*x <= 3; } void into2(int &x) { x*=2; } int main() { list<int> N1(10), N2(10); // N1 and N2 are both empty lists of 10 elements each generate_n(N1.begin(), 10, linspace); // N1 now contains 1,2,...,10 for_each(N2.begin(), remove_copy_if(N1.begin(), N1.end(), N2.begin(), sqrle3), into2); // N2 now contains 4,6,...,20 }
There is some effort in providing C++ with list-comprehension constructs/syntax similar to the set builder notation.
- In Boost.Range[1] library there is a notion of adaptors[2] that can be applied by to any range and do filtering, transformation etc. With this library, the original Haskell example would look like (using Boost.Lambda[3] for anonymous filtering and transforming functions):
counting_range(1,10) | filtered( _1*_1 > 3 ) | transformed(ret<int>( _1*2 ))
Full example is here: http://codepad.org/y4bpgLJu
- This [6] implementation uses a macro and overloads the << operator. It evaluates any expression valid inside an 'if', and any variable name may be chosen. It's not threadsafe, however. Usage example:
list<int> N; list<double> S; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) N.push_back(i); S << list_comprehension(3.1415 * x, x, N, x*x > 3)
- This [7] implementation provides head/tail slicing using classes and operator overloading, and the | operator for filtering lists (using functions). Usage example:
bool even(int x) { return x % 2 == 0; } bool x2(int &x) { x *= 2; return true; } list<int> l, t; int x, y; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) l.push_back(i); (x, t) = l | x2; (t, y) = t; t = l < 9; t = t < 7 | even | x2;
See also
- The SELECT statement together with its FROM and WHERE clauses in SQL
- Programming language
- Mathematical notation
- Monads in functional programming for monads and monadic notation in general
- For other programming language constructs used to process sequences:
- For other programming language constructs copied from the mathematical notation:
Notes and references
- ^ Comprehensions, a query notation for DBPLs
- ^ The functional guts of the Kleisli query system
- ^ Warsaw, Barry (2 October 2008). "PEP 202 – List Comprehensions". python.org. http://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0202/.
- ^ "2.1 Location Steps". XML Path Language (XPath). W3C. 16 November 1999. http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath#section-Location-Steps.
- ^ "XQuery FLWOR Expressions". W3Schools. http://www.w3schools.com/XQuery/xquery_flwor.asp.
- ^ "Single-variable List Comprehension in C++ using Preprocessor Macros". http://mfoliveira.org/blog/2011/01/04/simple-list-comprehension-in-cp-using-preprocessor-macros/.
- ^ "C++ list comprehensions". http://www.tedunangst.com/listcc.html.
- List Comprehension in The Free On-line Dictionary of Computing, Editor Denis Howe.
- Trinder, Phil (1992). "Comprehensions, a query notation for DBPLs". Proceedings of the third international workshop on Database programming languages: bulk types & persistent data, Nafplion, Greece. pp. 55–68. http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?coll=GUIDE&dl=GUIDE&id=135271.
- Wadler, Philip (1990). "Comprehending Monads". Proceedings of the 1990 ACM Conference on LISP and Functional Programming, Nice. http://citeseer.ist.psu.edu/wadler92comprehending.html.
- Wong, Limsoon (2000). "The Functional Guts of the Kleisli Query System". Proceedings of the fifth ACM SIGPLAN international conference on Functional programming. International Conference on Functional Programming. pp. 1–10. http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=351241&dl=ACM&coll=portal.
Haskell
- The Haskell 98 Report, chapter 3.11 List Comprehensions.
- The Glorious Glasgow Haskell Compilation System User's Guide, chapter 7.3.4 Parallel List Comprehensions.
- The Hugs 98 User's Guide, chapter 5.1.2 Parallel list comprehensions (a.k.a. zip-comprehensions).
OCaml
Python
- Python Reference Manual, chapter 5.2.4 List displays.
- Python Enhancement Proposal PEP 202: List Comprehensions.
- Python Reference Manual, chapter 5.2.5 Generator expressions.
- Python Enhancement Proposal PEP 289: Generator Expressions.
Common Lisp
- Implementation of a Lisp comprehension macro by Guy Lapalme
Clojure
Axiom
External links
- SQL-like set operations with list comprehension one-liners in the Python Cookbook
- Discussion on list comprehensions in Scheme and related constructs
- List Comprehensions across languages